- Real GDP growth in Africa resilient despite global uncertainty
- African banks optimistic about future development of local markets
- Small business, manufacturing and agriculture key focus of increased lending
The European Investment Bank today published the new edition of the “Banking in Africa” series: “Financing Transformation amid Uncertainty”. It is the fifth edition of this economic report that analyses recent developments in the African banking sectors. Based on both macroeconomic and survey data, the report addresses structural issues and investment opportunities in Africa and frames policy options for all stakeholders.
The new report combines in-house research with contributions from commercial banks operating across Africa, international financial institutions and other leading policy institutions including the OECD Development Centre and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
“The EIB is committed to investment in Africa in partnership with countries and industry across the continent. The EU Bank has been active in Africa since 1963 and provided a total of 45 billion Euro in financing since then. Our new report aims to share understanding and knowledge of African investment trends, and contribute to debate about best practice in investment and financing. Investments are essential for sustainable growth, prosperity, and social progress in Africa. As the European Union’s bank, we will continue to work together with our partners to support sustainable investments, foster inclusive and resilient growth, and reduce poverty,” said Werner Hoyer, President of the European Investment Bank.
Long-term strategy of African banking groups
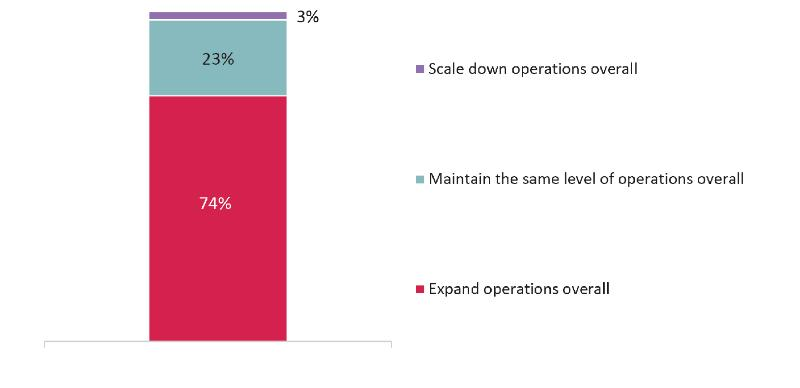
Source: 2019 EIB survey of African banking groups
Sustainable cities, boosting agricultural productivity and remittances
This year’s report includes detailed analysis on three issues crucial for Africa in the 21st century.
Firstly, the report explores policy options to finance urban development in the context of fast expanding African cities and highlights that adopting a territorial and inclusive approach is key to unleashing the potential of urbanisation in Africa.
Secondly, the report discusses the financing of Africa’s agricultural value chains and their potential to boost agricultural productivity, thereby supporting sustainable economic development.
Finally, the report examines how remittances can be harnessed to boost financial sector development,. It outlines how development of payment systems and increased competition in remittance markets is essential to bring down the cost of sending remittances and encourage remitters to use formal channels to send funds.
Economic growth and debt situation
The new study expected that economic growth in Africa is projected to accelerate moderately in 2020, due to strengthening demand. However, the current population growth rate means that GDP per capita will increase less than needed to ensure fast convergence with middle- and high-income economies, to make a significant dent in poverty and create enough jobs for the growing labour force. The average debt situation of African countries shows signs of stabilisation, but there is a high risk of debt distress in several countries due to the high level of government debt, particularly non-concessional debt, and rising debt-servicing costs. There is a significant degree of heterogeneity across countries regarding the pace of recovery, medium-term prospects and debt sustainability.
Development of African banking groups and markets
Taking stock of trends and strategic issues affecting banking groups in Africa, the report finds that the surveyed banking groups are cautiously optimistic about a gradual return to growth and stability in African banking markets. Nevertheless, some banks are still in consolidation mode, especially in the short term. Banking groups report improvements in terms of loan origination and funding conditions. Non-performing loans (NPLs) appear to be coming under control in most banking groups but they are still on the rise in others. Respondent banks are planning to expand their loan books, identifying manufacturing and agriculture as their top sectoral focuses at the moment. In addition, most banking groups report putting a very high priority on small and medium-sized company (SME) financing as a growth area. However, they also identify some specific constraints to lending to SMEs: shortage of bankable projects, lack of collateral of sufficient quality, SMEs’ lack of managerial capacity, informality and high default rates amongst SMEs.
African banking groups: Sector lending focus
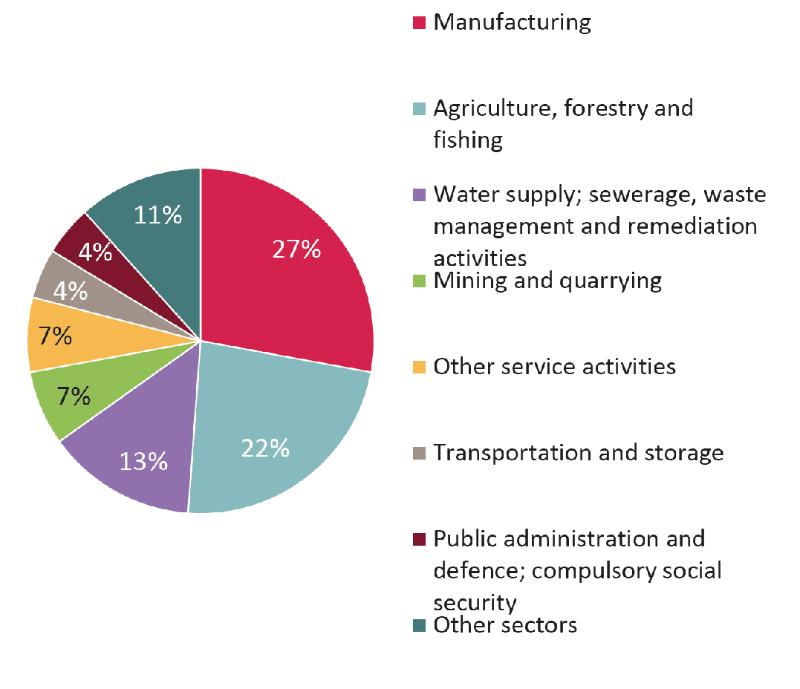
Source: 2019 EIB survey of African banking groups
Sustainable cities, boosting agricultural productivity and remittances
This year’s report also touches upon three thematic issues of cross-cutting importance in African countries.
Firstly, the report explores policy options to finance urban development in the context of fast expanding African cities and highlights that adopting a territorial and inclusive approach is key to unleashing the potential of urbanisation in Africa. Secondly, the report discusses the financing of Africa’s agricultural value chains and their potential to boost agricultural productivity, thereby supporting sustainable economic development. Finally, the report examines how remittances can be harnessed to boost financial sector development, e.g. by developing payment systems and promoting competition in remittance markets to bring down the cost of sending remittances and encourage remitters to use formal channels to send funds.
Background information
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the long-term lending institution of the European Union owned by its Member States. It makes long-term finance available for sound investment in order to contribute towards EU policy goals. The Banking in Africa report is a product of the EIB Economics Department, providing an analysis of recent development in the African banking sectors and specific structural topics of relevance. It combines in-house research with contributions by leading market experts from commercial banks operating in the region, international financial institutions, development institutions and others.
Chapter overview “Banking in Africa: Financing Transformation amid Uncertainty”
The first part of the report represents a study of the banking sectors across Africa. The second part consists of thematic chapters that address transversal challenges and opportunities with regard to financing investment in Africa.
Chapter 1 reports on the responses to a survey of banking groups in Africa.
Chapters 2-6 examine recent trends in the banking sectors in, respectively, Northern Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa and Southern Africa.
Chapter 7 concerns the opportunities and challenges associated with investing sustainably in Africa’s cities.
Chapter 8 analyses how well-structured agricultural value chain financing can boost agricultural productivity, thereby supporting sustainable economic development in Africa.
Chapter 9 discusses how remittances can become an even more effective driver of economic and social development on the continent.
Chapter 10 summarises how the EIB has been investing in sustainable development across Africa since 1963, explaining the type of financial support and technical assistance offered by the EIB to financial sectors on the continent and briefly exploring the way forward.
